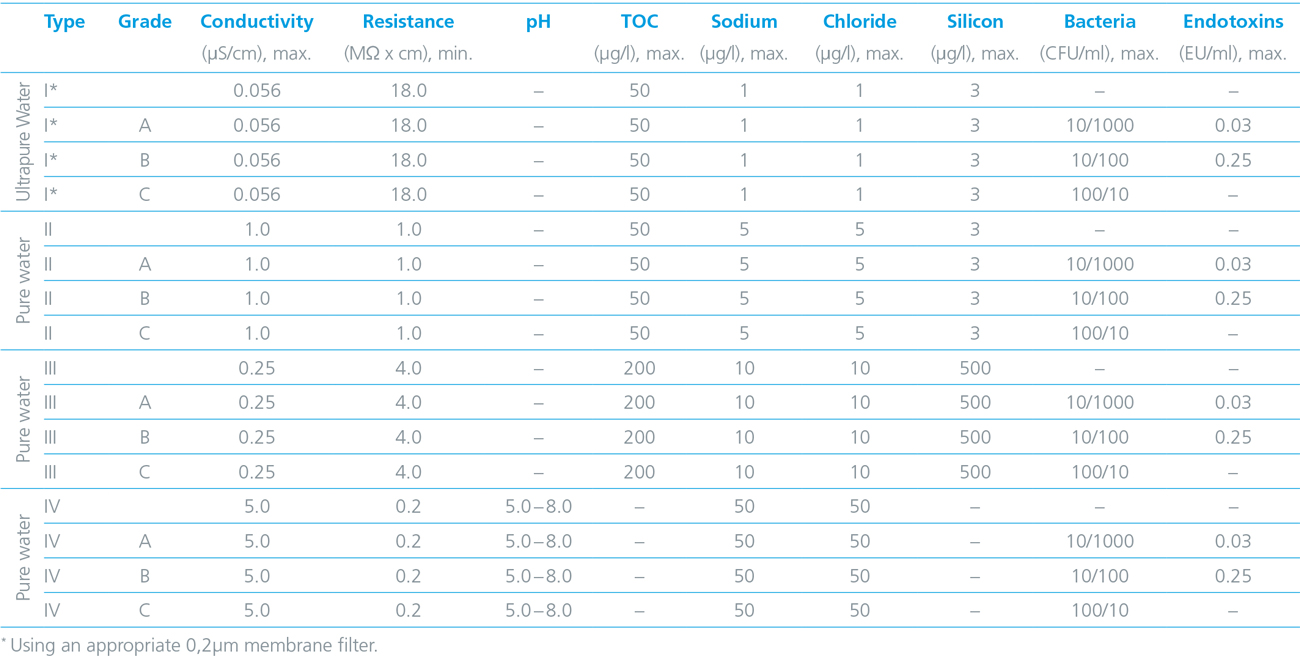
Water quality standards
For various fields of use and requirements.
International Organization for Standardization (ISO)
ISO 3696:1987 distinguishes between three degrees of purity for water for analytical purposes in laboratories.
| pH value at 25°C | – | – | 5.0 up to 7.0 |
| Conductivity at 25 °C [µS/cm] | 0.1 | 1.0 | 5.0 |
| Oxidizable matter, oxygen content [mg/l, max.] | – | 0.08 | 0.4 |
| Absorption at 254 nm and a lenght of 1 cm (absorption units, max.) | 0.001 | 0.01 | – |
| Residue after evaporation by heating to 110 °C (mg/kg, max.) | – | 1 | 2 |
| Silicon content [mg/l, max.] | 0.01 | 0.02 | – |
Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI)
This institute defined the quality requirements of water for clinical laboratories. The regulations that were valid up to 2006 (NCCL types 1, 2 and 3) but were then invalidated by the requirement that water must be suitable for the intended usage. Only the degree of purity of so-called “Clinical laboratory reagent water” (CLRW) is described.
| Resistance [MΩ x cm] | 10 |
| TOC [ppb] | < 500 |
| Bacteria [CFU/ml] | < 10 |
| Particle Content | Inline 0.2 µm-filter |
American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM)
The ASTM D1193-06 (2011) deals with the requirements for chemical analyses and physical tests.